MariaDB
What is MariaDB
Introduction to MariaDB
MariaDB is a community-developed, commercially supported fork of the MySQL relational database management system (RDBMS), intended to remain free and open-source software under the GNU General Public License. Development is led by some of the original developers of MySQL, who forked it due to concerns over its acquisition by Oracle Corporation in 2009.
MariaDB is intended to maintain high compatibility with MySQL, with library binary parity and exact matching with MySQL APIs and commands, allowing it in many cases to function as drop-in replacement for MySQL. However, new features are diverging.[7] It includes new storage engines like Aria, ColumnStore, and MyRocks.
Its lead developer/CTO is Michael "Monty" Widenius, one of the founders of MySQL AB and the founder of Monty Program AB. On 16 January 2008, MySQL AB announced that it had agreed to be acquired by Sun Microsystems for approximately $1 billion. The acquisition completed on 26 February 2008. Sun was then bought the following year by Oracle Corporation. MariaDB is named after Widenius' younger daughter, Maria. (MySQL is named after his other daughter, My.)
Licensing
The MariaDB Foundation mentions:
MariaDB Server will remain Free and Open Source Software licensed under GPLv2, independent of any commercial entities.
Third-party software
MariaDB's API and protocol are compatible with those used by MySQL, plus some features to support native non-blocking operations and progress reporting. This means that all connectors, libraries and applications which work with MySQL should also work on MariaDB—whether or not they support its native features. On this basis, Fedora developers replaced MySQL with MariaDB in Fedora 19, out of concerns that Oracle was making MySQL a more closed software project. OpenBSD likewise in April 2013 dropped MySQL for MariaDB 5.5.
However, for recent MySQL features, MariaDB either has no equivalent yet (like geographic function) or deliberately chose not to be 100% compatible (like GTID, JSON).[35] The list of incompatibilities grows longer with each version.[36]
What is NoSQL
Introduction to NoSQL
As already said NoSQL is a non relational database that provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data. NoSQL databases are used in real-time web applications and big data and their use are increasing over time.
NoSQL systems are also sometimes called Not only SQL to emphasize the fact that they may support SQL-like query languages.
A NoSQL database includes simplicity of design, simpler horizontal scaling to clusters of machines and finer control over availability.
The data structures used by NoSQL databases are different from those used by default in relational databases which makes some operations faster in NoSQL.
When should NoSQL be used
- When huge amount of data need to be stored and retrieved.
- The relationship between the data you store is not that important.
- The data changing over time and is not structured.
- Support of Constraints and Joins is not required at database level.
- The data is growing continuously and you need to scale the database regular to handle the data.
How to install it
Getting Started
There are two ways to work with MongoDB on your computer locally.
MongoDB with GUI
To install MongoDB locally you have to go to the MongoDB website and download the Community version for your operating system.
Once downloaded you have to extract the folder and open the "install_compass" file.
Now the GUI for MongoDB is installed.
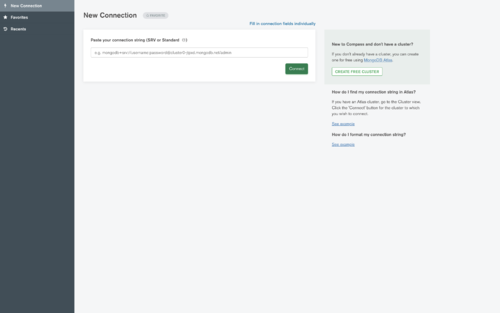
If you don't want to install MongoDB via terminal skip the next step.
MongoDB with Terminal
To install MongoDB locally over Terminal you have to go to the MongoDB website choose your operating system and follow the construction to add it on your Terminal.
Now the Terminal version for MongoDB is installed.
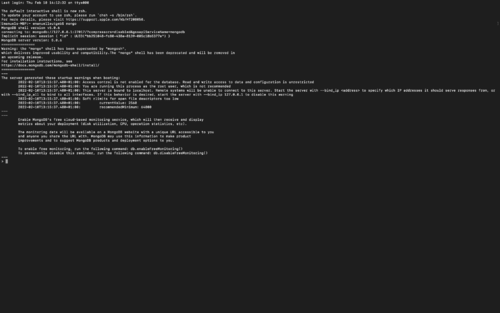
Working with MongoDB
Create your first Database
I highly recommend to use the Mongo Compass.
So to connect to the localhost just click "Connect" and the app will connect you to your localhost.

Now you can easy create a new database.
- Click "Create database".

- Give the Database a name and the Collection too, like "TENNIS" and "PLAYERS".
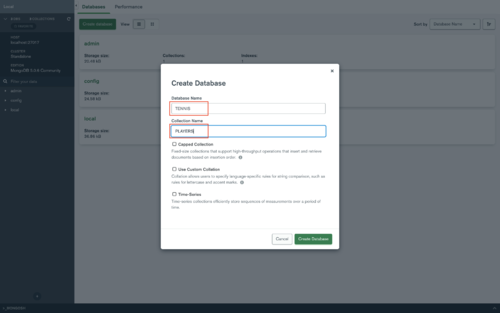
- Click now on the Database which was created by you for example "TENNIS".
- Click "Create collection".
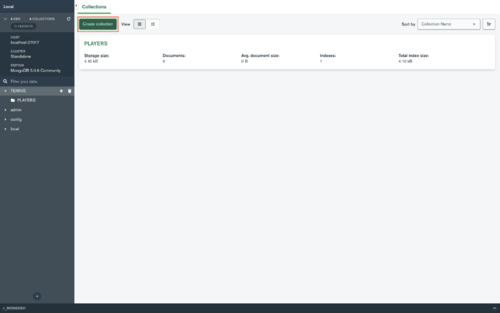
- Give the Collection a name, like "TEAMS".
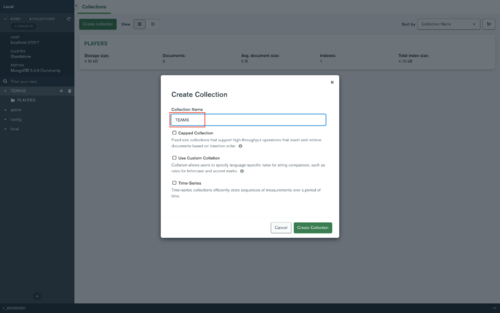
Insert your first Data
After you create the database and all of your collections, you can start inserting data to it.
- Click on a Collection where you want to add some data for EXAMPLE "PLAYERS".
- Click now on "ADD DATA" and then on "Insert Document".
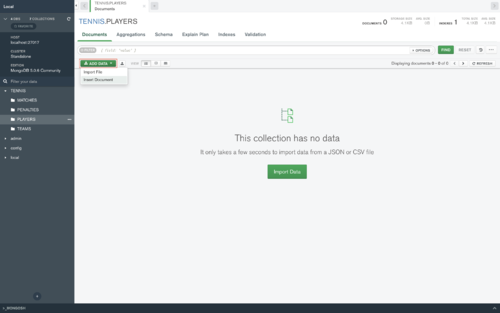
- Now you can add your data inside.
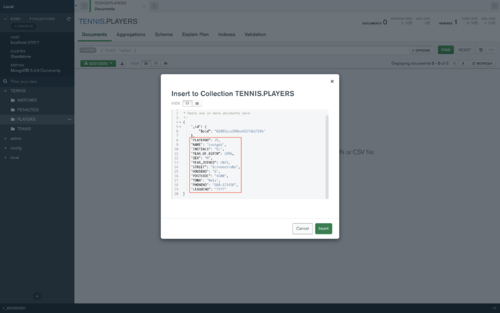
- But you also can add an existing file into it
click on "ADD DATA" and then on "Import File".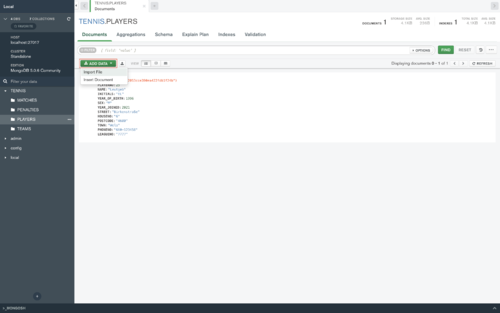
- Now you can choose your file, the type and then import it to your Database.
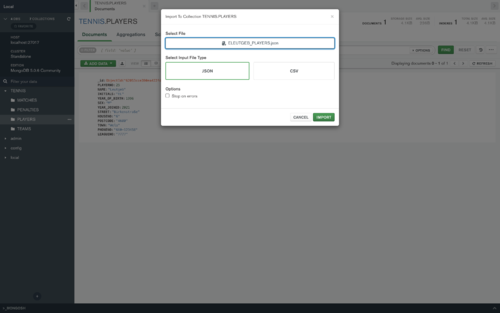
Create your first Query
After you import or insert all your data into the database you can start making some queries.
Just click on the "FILTER" type in your query and press "FIND". 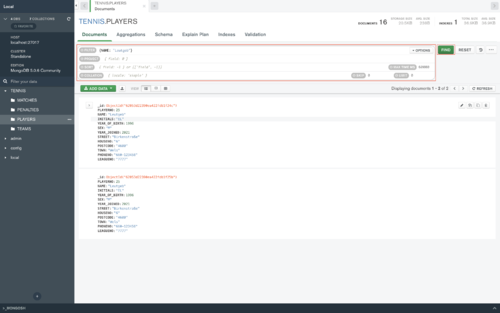
For more information how to use it please visit the MongoDB manual.
Made with ♥︎ by Emanuel Leutgeb